How TCM Understands and Treats Dampness
“Nine Out of Ten People Are Damp”: The Hidden Danger of Dampness in Chinese Medicine
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), there’s a common saying: “Nine out of ten people have dampness.” Dampness is more than a seasonal issue—it’s often an underlying root of many chronic conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, fatty liver, cancer, rheumatoid conditions, gout, and even stroke.
If dampness is not eliminated, long-term health problems may raised. Take care now to clear dampness, calm the Heart, and support digestion, so your energy doesn’t get overwhelmed in the next season.
Dampness is one of the six pathogenic factors in TCM (wind, cold, summer heat, dampness, dryness, fire). It is heavy, sticky, obstructive, and difficult to eliminate. It easily blocks the flow of Qi and impairs digestive function, especially the Spleen.
Key characteristics:
-
Often combines with other pathogens like wind, cold, or heat, making symptoms more complex:
Wind-Damp: joint pain and stiffness
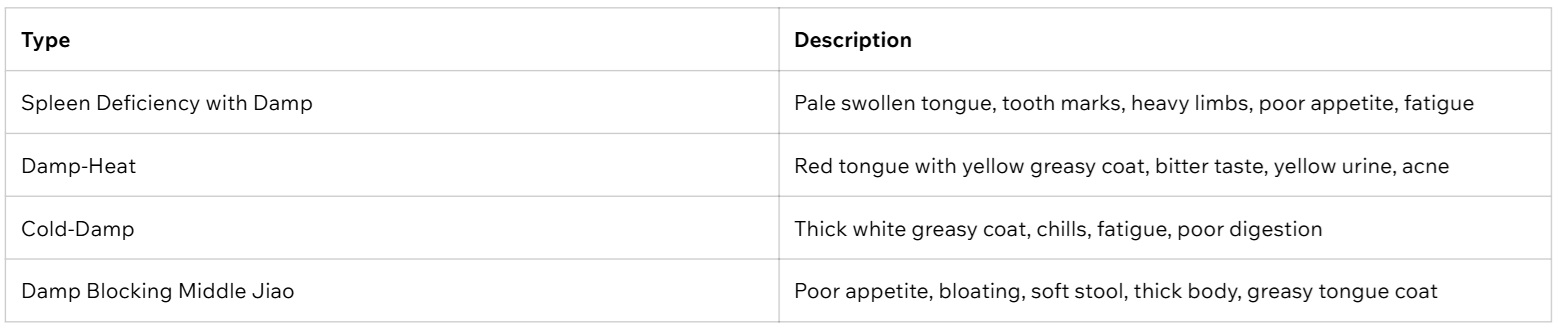
Cold-Damp: loose stools, chills, fatigue
Damp-Heat: acne, eczema, bitter taste, sticky stools
Hard to eliminate — “Cold is easy to clear, dampness is stubborn.” Like oil soaked into flour, it lingers and is hard to transform.
Typical Presentations of Dampness
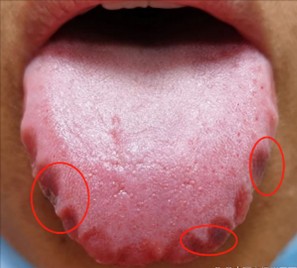
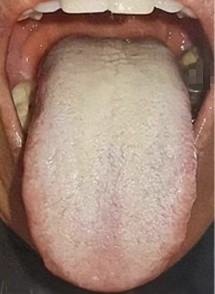
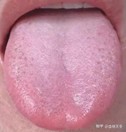
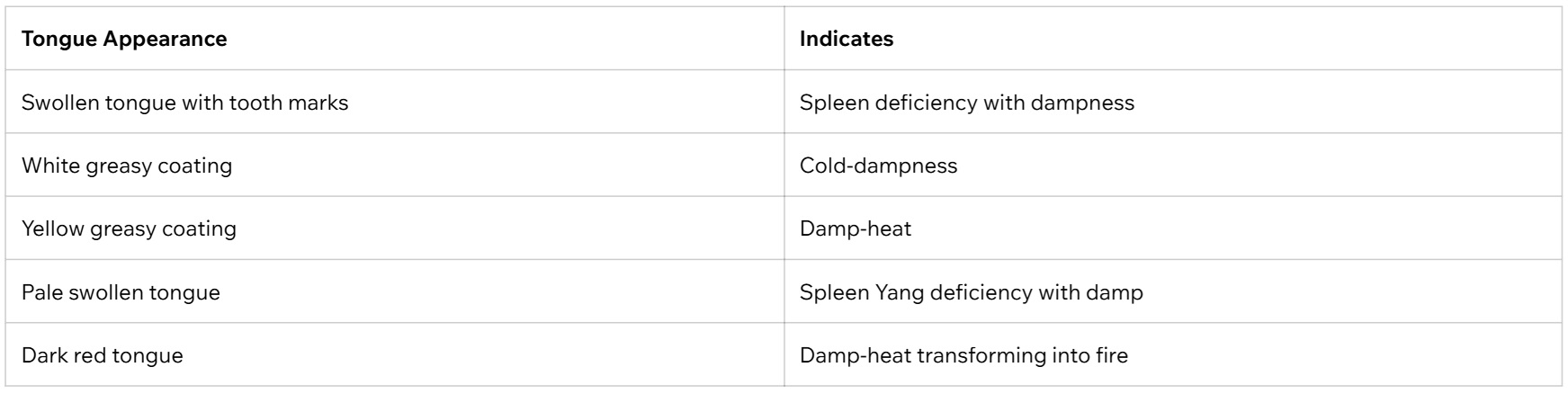
1. Tongue Diagnosis
The first two images show typical tongue appearances associated with internal dampness. The third image illustrates a normal tongue.
2. Systemic Symptoms
Digestive:
Poor appetite, bloating after meals
Sticky, unformed stools
Nausea, reflux, greasy taste in the mouth
Dark yellow urine, low volume
Body sensations:
Heavy limbs, chest tightness, foggy head
Oily skin, acne, eczema
Puffy legs, fatigue that lingers even after sleep
Women-specific:
Yellowish, excessive vaginal discharge
Heavy or dark menstrual flow with clots
Abdominal heaviness and fatigue during menstruation
Mental state:
Slow thinking, low motivation
Depression, irritability, frequent sighing
Daytime sleepiness, poor concentration
Five Levels of Dampness
Five Levels of Dampness Severity (from surface to deep)

The deeper the dampness, the longer and harder it is to treat. Pattern differentiation and system-based healing are essential.
Common Dampness Syndromes in TCM:
Where Does Dampness Come From?
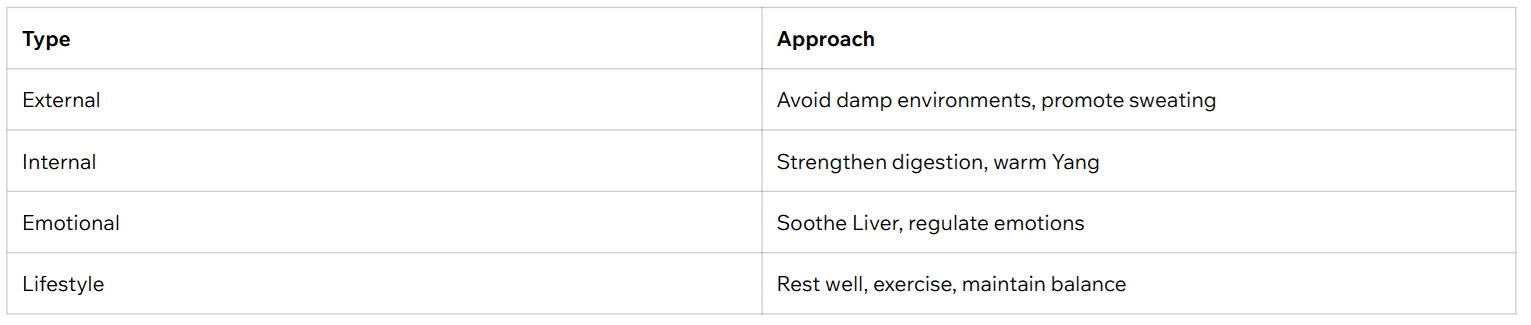
Dampness can originate from external sources or internal imbalances, and often both play a role.
🏞 External Dampness
Caused by environmental exposure—especially common in humid, rainy, or poorly ventilated environments.
Common triggers:
Climate: rainy season, foggy or humid areas
Jobs with water exposure: kitchens, seafood handlers, salons, etc.
Lifestyle: sleeping with wet hair, wearing damp clothes, not drying off after getting wet
Home: basements, closed windows, moldy spaces, air conditioning overuse
Even in dry climates, internal dampness is possible due to poor diet or weak digestion.
🧬 Internal Dampness
Caused by dysfunction of the Spleen system. When the Spleen fails to transform and transport fluids, dampness accumulates internally.
📌 Five Common Causes of Dampness
-
Emotional strain:
Anger → Liver Qi stagnation → damp-heat in Liver/Gallbladder
Overthinking → weakens Spleen → internal dampness
Chronic stress/anxiety → disrupts fluid distribution
-
Poor diet:
Too much cold/raw foods → weakens digestive fire
Oily, spicy, fried food and alcohol → creates damp-heat
Irregular eating or overeating → overloads the Spleen
-
Medications:
Long-term drug use (especially for hypertension, diabetes) can impair liver/gallbladder function and create damp-heat.
-
Environmental exposure:
Living in damp homes, overuse of humidifiers, summer humidity
-
Poor lifestyle:
Late nights → damages Liver function → leads to damp-heat
Lack of movement → no sweating → damp stagnation
Constant air conditioning → pores closed, damp retained
“Movement generates Yang” — modern sedentary lifestyles and sleep deprivation are major causes of internal dampness.
Conclusion
Dampness has complex origins and must be addressed holistically.